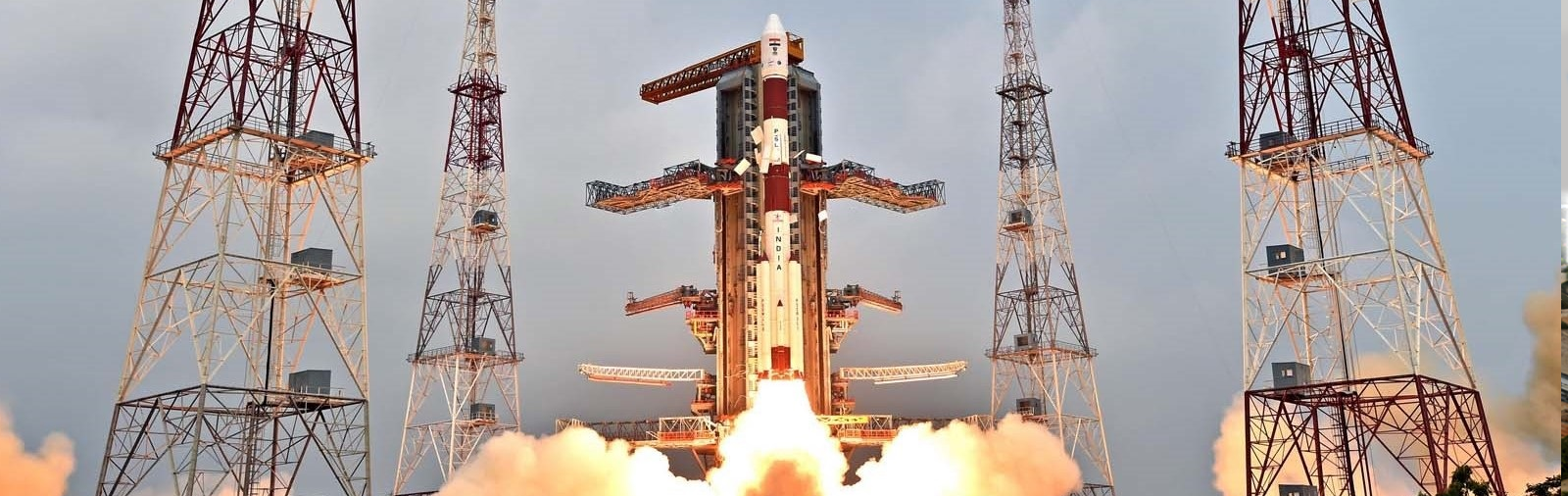
ISRO has been providing Launch services for customer satellites since 1999 onboard ISRO’s Polar Satellite Vehicle (PSLV). Till June 2019, 319 customer satellites from 33 countries have been launched onboard PSLV on commercial basis through its commercial arm . In September 2016, PSLV C-37 has successfully injected 104 satellites into orbit – the highest number of satellites launched in a single mission so far. PSLV is a versatile vehicle, capable of launching satellites into LEO, SSO, Sub-GTO, GTO Orbits.
With ISRO operationalising its Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle (GSLV) and GSLV Mk-III and building Small Satellite Launch Vehicle (SSLV), as a launch on demand Vehicle, NSIL is in a position to offer and expand its launch services. The launches will be accomplished from Satish Dhawan Space Centre (SDSC), India’s Spaceport, located at Sriharikota, near Chennai.
Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle (GSLV) employing cryogenic stage is intended to carry heavier satellites of the order of 2200 kg into the Geosynchronous Transfer Orbits (GTO). The heavy lift launcher GSLV MkIII (alias LVM3) is intended to enhance the GTO capability to 4000 kg and is currently under development. The Small Satellite Launch Vehicle (SSLV) is intended to carry 500 kg satellite to 500km LEO Orbit.
With the suite of launch vehicles developed and operationalised by ISRO, NSIL offers comprehensive launch solutions – for both Ride Sharing and Dedicated Missions – with a wide variety of flight proven payload separation systems and adaptors developed in-house for all category of satellites. For more details on payload separation system Click here.